“I don’t need a hard disk in my computer if I can get to the server faster… carrying around these non-connected computers is byzantine by comparison.” – Steve Jobs, Co-founder, CEO, and Chairman, Apple Inc.
Introduction
In the last decade, online work has increased manifold and now online space crunch is occurring with multinationals and tech giants. So with every problem, there is always a solution associated with it. To resolve the digital space crunch problem solver was cloud computing. Clouds offer access to data anytime anywhere, irrespective of any system and place. By this, work culture in business/organizations is speeding. And employees are free to work remotely. With the help of cloud computing, people found a better way to run the business.
Cloud computing
Cloud computing can be defined as the delivery of computing services such as servers, databases, storage to application, processing power, networking over the internet on a payment basis. Cloud computing is internet-based computing that contains a large group of servers or should say a large group of remote servers which are connected to a network that allows a centralized database to store required things from an organization.
AWS (Amazon Web Service)
“There is an incredible amount of data growth and the old tools and the old data stores that existed the last 20-30 years are not going to be able to handle this. Every type of data store is being reinvented and will be reinvented multiple times,” – Andy Jassy, AWS CEO
AWS (Amazon Web Service) is a subsidiary of amazon.com and is one of the secure cloud computing service platforms which offers database, computing power, easy to use, and flexible cloud computing solutions on subscription.
AWS provides:
- Infrastructure as a Service so users need not think about the backup and power supply of the service
- Platforms as a service, so users need not be worried about the platforms used such as java, PHP.
- Software of the Service where users need not worry about the technicalities of the software application.
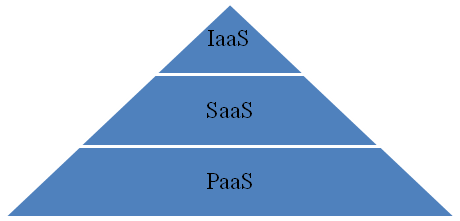
Saas (Software as a Service) – SaaS is an on-demand service. In this service, the user needs to utilize the end product that is the final software. SaaS is mostly used by the end-user and needs to pay per use of the application to the vendors. An end-user could be anyone with or without technical knowledge. SaaS is a platform-independent service and is available for multiple users.
Major examples of SaaS – The Google ecosystem such as Gmail, Docs, Drive
Pros – Accessible remotely and need to commute to use the same
Cons – Need high-speed internet to use most of the software
PaaS (Platform as a Service) – This is a service that provides a runtime environment. Used by developers to develop the software/application, where the users (developer) offer development and deployment tools, access to the user interface, access to an application, access related data. Using PaaS as a service users can build compile and run their programs. In this service user can just manage data and the application resource; the rest all the resources are managed by the vendor.
Major examples of PaaS – AWS (Amazon Web Service); Google App Engine, Windows Azure.
Pros – Cost-effective services. The deliverables are also fast due to fast development.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) – In this service, the users have maximum freedom to manage things. They can firstly decide on which Operating System they are going to work. This service provides the basic model of infrastructure and computer architecture, virtual machines, and storage to store data and IP addresses. This model is mainly used by the System Administrators.
The major example of IaaS – Amazon EC2, RackSpace.com; Go Grid.
Pros – Enhanced Scalability.
History of AWS
This timeline will help in understanding the evolution of AWS:
- 2002- AWS Service launched
- 2006- Services such as S3, EC2, etc launched
- 2009- VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) launched
- 2012- AWS first conference, where AWS got its first customer
- 2015- Profit of USD 6.2 billion
- 2019- AWS released almost 100 clouds
Reasons Why User Demands AWS?
Most of the organizations are trying to use AWS; everyone tries to put their application on the cloud. The reason, due to which AWS is a top provider and provides per-hour billing to the user, is very transparent. The sign-up process is very easy and user-friendly. Billing is simple and users can extract the reports according to their usage. AWS is the most reliable and popular cloud service amongst all other cloud services and has high stability of services.
Typical Services by AWS:
- EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud)
- VPC (Virtual Private Cloud)
- S3 (Simple Storage Service)
- RDS (Relational Database Service)
- Route 53
- ELB (Elastic Load Balancing)
- Autoscaling
Companies Using AWS
Adobe, BMW, Canon, Disney, ESPN, Financial Times, GoSquared, HTC, IMDb, Johnson & Johnson, Kellogg’s, Lamborghini, McDonald’s, NASA, Philips, Pinterest, Samsung
Conclusion
It can be said that AWS has many benefits being comprehensive, cost-effective, adaptable, secure, improved productivity, innovative, global leader. With AWS, you can improve your ability to meet core security and compliance requirements, such as data locality, protection, and confidentiality with our comprehensive services and features.
References for more read:
https://www.simplilearn.com/tutorials/aws-tutorial/what-is-aws
https://www.contino.io/insights/whos-using-aws
https://www.impigertech.com/resources/blogs/benefits-of-aws
https://aws.amazon.com/security/
*********************************